模板指令¶
文档的这一部分是对不同模板指令的介绍。将提供简单功能和复杂功能的示例。指令的语法在基于XML的模板和基于JSON的模板之间略有不同。
这些示例将主要针对GeoJSON和GML提供。但是,除非另行指定,否则为GeoJSON输出定义的语法对JSON-LD模板有效
模板指令摘要¶
以下是所有模板指令的摘要,旨在供快速参考。以下各节详细解释了每个指令。
基于JSON的模板¶
以下是基于JSON的模板中提供的指令。
Usage |
Syntax |
Description |
属性内插 |
${Property} |
将其指定为属性值 ( |
CQL评估 |
$${cql} |
将其指定为元素值 ( |
设置子属性的求值上下文。 |
${SOURCE}。 |
将其指定为数组中的第一个嵌套对象 ( |
过滤数组、对象、属性 |
$Filter |
specify it inside the first nested object in arrays ( |
定义用于在要素范围之外自定义输出的选项 |
$Options |
在JSON模板顶部将其指定为JSON对象(GeoJSON选项: |
允许将一个模板包含到另一个模板中 |
$INCLUDE、$INCLUDE平面 |
指定 |
允许一个模板扩展另一个模板 |
$Merge |
指定 |
允许对空值进行编码。默认设置为未编码。 |
${Property}!或$${表达式}! |
好了!在属性内插或cql指令的末尾 ( |
基于XML的模板¶
以下是基于XML的模板中提供的指令。
Usage |
Syntax |
Description |
属性内插 |
${Property} |
将其指定为元素值 ( |
CQL评估 |
$${cql} |
将它们指定为元素值 ( |
为子元素中的属性内插和CQL求值设置求值上下文。 |
GFT:来源 |
将其指定为XML属性 ( |
根据定义的条件过滤要应用的元素 |
GFT:滤镜 |
将其指定为要过滤的元素的XML属性 ( |
标记XML模板的开始。 |
GFT:模板 |
它必须是XML模板的根元素 ( |
定义用于在要素范围之外自定义输出的选项 |
GFT:选项 |
将其指定为XML文档开头的元素 |
允许将一个模板包含到另一个模板中 |
$INCLUDE,GFT:INCLUDE平面 |
指定 |
允许对空值进行编码。默认设置为未编码。 |
${Property}! |
将其指定为元素值 ( |
功能模板语法分步介绍¶
本简介旨在说明可在模板中使用的不同指令。为清楚起见,文档将以 Simple Feature 示例,然后通过 Complex Feature 举个例子。但是,将显示的所有指令都适用于简单功能和复杂功能。 GeoJSON 和 GML 将主要使用示例。为 JSON-LD 输出格式定义模板的规则与 GeoJSON 模板,但有两个例外:
A
@context需要指定(请参阅options下一节)。该标准要求属性值都是字符串。
${Property}和$${cql}指令(简单功能示例)¶
GeoJSON¶
假设我们想要更改 topp:states 一层。默认输出中的单个要素如下所示:
{
"type": "Feature",
"id": "states.1",
"geometry": {},
"geometry_name": "the_geom",
"properties": {
"STATE_NAME": "Illinois",
"STATE_FIPS": "17",
"SUB_REGION": "E N Cen",
"STATE_ABBR": "IL",
"LAND_KM": 143986.61,
"WATER_KM": 1993.335,
"PERSONS": 11430602,
"FAMILIES": 2924880,
"HOUSHOLD": 4202240,
"MALE": 5552233,
"FEMALE": 5878369,
"WORKERS": 4199206,
"DRVALONE": 3741715,
"CARPOOL": 652603,
"PUBTRANS": 538071,
"EMPLOYED": 5417967,
"UNEMPLOY": 385040,
"SERVICE": 1360159,
"MANUAL": 828906,
"P_MALE": 0.486,
"P_FEMALE": 0.514,
"SAMP_POP": 1747776
}
}
特别是,我们希望在最终输出中只包含某些属性(例如,几何图形、州名称、代码、有关人口、男性、女性和工人的值)。我们还希望更改一些属性名称,并使其大小写。最后,我们希望有一个具有几何图形WKT表示的字符串字段。所需输出如下所示:
{
"type":"Feature",
"id":"states.1",
"geometry":{
"type":"MultiPolygon",
"coordinates":"[....]"
},
"properties":{
"name":"Illinois",
"region":"E N Cen",
"code":"IL",
"population_data":{
"population":114306027,
"males":5552233.0,
"females":5878369.0,
"active_population":4199206.0
},
"wkt_geom":"MULTIPOLYGON (((37.51099000000001 -88.071564, [...])))"
}
}
这样的模板将允许我们生成上面的输出:
{
"type": "Feature",
"id": "${@id}",
"geometry": "${the_geom}",
"properties": {
"name": "${STATE_NAME}",
"region": "${SUB_REGION}",
"code": "${STATE_ABBR}",
"population_data":{
"population": "${PERSONS}",
"males": "${MALE}",
"females": "${FEMALE}",
"active_population": "${WORKERS}"
},
"wkt_geom":"$${toWKT(the_geom)}"
}
}
可以看到,新输出具有在模板中定义的属性名称。此外, population 相关属性被放置在嵌套的json对象中。最后,添加了具有WKT几何表示的wkt_geom属性。
GML¶
相同的模板机制可以应用于GML输出格式。这是一个GML模板示例,同样适用于 topp:states 图层
<gft:Template>
<gft:Options>
<gft:Namespaces xmlns:topp="http://www.openplans.org/topp"/>
<gft:SchemaLocation xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.opengis.net/wfs/2.0 http://brgm-dev.geo-solutions.it/geoserver/schemas/wfs/2.0/wfs.xsd http://www.opengis.net/gml/3.2 http://schemas.opengis.net/gml/3.2.1/gml.xsd"/>
</gft:Options>
<topp:states gml:id="${@id}">
<topp:name code="${STATE_ABBR}">${STATE_NAME}</topp:name>
<topp:region>${SUB_REGION}</topp:region>
<topp:population>${PERSONS}</topp:population>
<topp:males>${MALE}</topp:males>
<topp:females>${FEMALE}</topp:females>
<topp:active_population>${WORKERS}</topp:active_population>
<topp:wkt_geom>$${toWKT(the_geom)}</topp:wkt_geom>
</topp:states>
</gft:Template>
这就是功能的显示方式:
<topp:states gml:id="states.10">
<topp:name code="MO">Missouri</topp:name>
<topp:region>W N Cen</topp:region>
<topp:population>5117073.0</topp:population>
<topp:males>2464315.0</topp:males>
<topp:females>2652758.0</topp:females>
<topp:active_population>1861192.0</topp:active_population>
<topp:wkt_geom>MULTIPOLYGON (([....])))</topp:wkt_geom>
</topp:states>
由于可以看到几何体仅被编码为WKT,而且STATE_ATTR值现在作为元素的XML属性出现 topp:states 。最后,没有在模板中定义的元素没有出现。
查看这些示例,可以看到可以定制输出的其他指令:
可以使用以下指令调用属性内插
${property_name}。在需要复杂运算的情况下,可以通过
$${cql}语法(支持所有CQL函数)。简单文本值在最终输出中按原样复制。
最后,GML模板需要将实际模板内容包装到
gft:Template元素。这个gft不需要绑定到命名空间。它只是用作与功能模板相关的元素的标记,不会出现在最终输出中。还有另一个元素,
gft:Options,里面还有另外两个元素。它将在后面的专门部分中进行解释。
源和过滤器(复杂要素示例)¶
GeoJSON¶
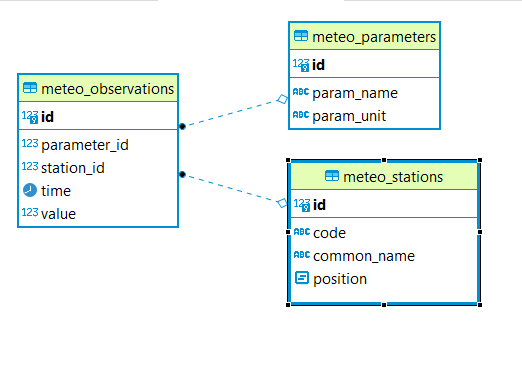
现在让我们假设已经配置了AppSchema层,并且需要定制复杂的功能输出。我们将以Meteo Station用例为例。有关用例的描述,请查看以下地址的文档 智能数据加载器扩展 。这是用例的域模型:
默认的GeoJSON输出格式会生成如下功能:
{
"type":"Feature",
"id":"MeteoStationsFeature.7",
"geometry":{
},
"properties":{
"@featureType":"MeteoStations",
"id":7,
"code":"BOL",
"common_name":"Bologna",
"meteoObservations":[
{
"id":3,
"time":"2016-12-19T11:28:31Z",
"value":35,
"meteoParameters":[
{
"id":1,
"param_name":"temperature",
"param_unit":"C"
}
]
},
{
"id":4,
"time":"2016-12-19T11:28:55Z",
"value":25,
"meteoParameters":[
{
"id":1,
"param_name":"temperature",
"param_unit":"C"
}
]
},
{
"id":5,
"time":"2016-12-19T11:29:24Z",
"value":80,
"meteoParameters":[
{
"id":2,
"param_name":"wind speed",
"param_unit":"Km/h"
}
]
},
{
"id":6,
"time":"2016-12-19T11:30:26Z",
"value":1019,
"meteoParameters":[
{
"id":3,
"param_name":"pressure",
"param_unit":"hPa"
}
]
},
{
"id":7,
"time":"2016-12-19T11:30:51Z",
"value":1015,
"meteoParameters":[
{
"id":3,
"param_name":"pressure",
"param_unit":"hPa"
}
]
}
]
}
}
上面的JSON有一个数据结构,其中:
Station对象具有嵌套的观测值数组。
每个观测都有一个描述观测类型的参数数组。
现在,让我们假设需要生成不同的输出,其中不是将通用的观测数组嵌套到根对象中,而是分别为每种类型的参数提供数组,例如温度、压力和WINDS_SPEED观测。换句话说,应该在属性名中直接提供信息,而不是在嵌套的参数对象中定义观察类型。所需的输出如下所示:
{
"type":"FeatureCollection",
"features":[
{
"Identifier":"MeteoStationsFeature.7",
"geometry":{
"type":"Point",
"coordinates":[
44.5,
11.34
]
},
"properties":{
"Name":"Bologna",
"Code":"STATION-BOL",
"Location":"POINT (44.5 11.34)",
"Temperatures":[
{
"Timestamp":"2016-12-19T11:28:31.000+00:00",
"Value":35.0
},
{
"Timestamp":"2016-12-19T11:28:55.000+00:00",
"Value":25.0
}
],
"Pressures":[
{
"Timestamp":"2016-12-19T11:30:26.000+00:00",
"Value":1019.0
},
{
"Timestamp":"2016-12-19T11:30:51.000+00:00",
"Value":1015.0
}
],
"Winds_speed":[
{
"Timestamp":"2016-12-19T11:29:24.000+00:00",
"Value":80.0
}
]
}
}
],
"totalFeatures":3,
"numberMatched":3,
"numberReturned":1,
"timeStamp":"2021-07-13T14:00:19.457Z",
"crs":{
"type":"name",
"properties":{
"name":"urn:ogc:def:crs:EPSG::4326"
}
}
}
这样的模板将允许生成这样的输出:
{
"$source":"st:MeteoStationsFeature",
"Identifier":"${@id}",
"geometry":"${st:position}",
"properties":{
"Name":"${st:common_name}",
"Code":"$${strConcat('STATION-', xpath('st:code'))}",
"Location":"$${toWKT(xpath('st:position'))}",
"Temperatures":[
{
"$source":"st:meteoObservations/st:MeteoObservationsFeature",
"$filter":"xpath('st:meteoParameters/st:MeteoParametersFeature/st:param_name') = 'temperature'"
},
{
"Timestamp": "${st:time}",
"Value": "${st:value}"
}
],
"Pressures":[
{
"$source":"st:meteoObservations/st:MeteoObservationsFeature",
"$filter":"xpath('st:meteoParameters/st:MeteoParametersFeature/st:param_name') = 'pressure'"
},
{
"Timestamp": "${st:time}",
"Value": "${st:value}"
}
],
"Winds_speed":[
{
"$source":"st:meteoObservations/st:MeteoObservationsFeature",
"$filter":"xpath('st:meteoParameters/st:MeteoParametersFeature/st:param_name') = 'wind speed'"
},
{
"Timestamp": "${st:time}",
"Value": "${st:value}"
}
]
}
}
除 ${property} 和 $${cql} 指令,还有两个指令:
在上面的示例中,
xpath('xpath')函数用于引用属性。在处理复杂要素时,必须在引用$filter或者是$${cql}指令。$source它旨在提供计算嵌套元素属性和XPATH所依据的上下文。在本例中,"$source":"st:meteoObservations/st:MeteoObservationsFeature"提供嵌套属性的上下文,指令将在该上下文中求值。在定义$source对于JSON数组,它应该在JSONObject中提供,该JSONObject与映射嵌套特征属性的JSON对象分开,如上例所示。在定义$source对于JSONObject,可以简单地将其作为对象属性添加(参见下面的示例)。使用时
${property}指令或一个xpath('xpath')函数可以引用绑定到大写字母的属性$source使用../记数法。${../previousContextValue}。$filter提供了筛选将包括在要应用到的元素中的值的可能性,在本例中为json数组。例如,过滤器$filter":"xpath('st:meteoParameters/st:MeteoParametersFeature/st:param_name') = 'wind speed'在Winds_speed数组允许根据param_name value。
关于源头,有一点要注意。仅当参照嵌套特征时才严格需要。这意味着在GeoJSON模板示例中 "$source":"st:MeteoStationsFeature" 可能被遗漏了。这不适用于嵌套元素定义,其中 "$source":"st:meteoObservations/st:MeteoObservationsFeature" 是强制性的。
下面是JSON模板位的列表,其中显示了 filters 不同于JSON数组的上下文中的定义,以及 $source JSONObject的定义。
对象(仅当st:值大于75.3时才对JSON对象进行编码)。
{
"Observation":
{
"$source":"st:MeteoObservationsFeature",
"$filter":"st:value > 75.3 ",
"Timestamp":"${st:time}",
"Value":"${st:value}"
}
}
属性(仅当st:值大于75.3时才编码时间戳属性)。
{
"Observation":
{
"$source":"st:MeteoObservationsFeature",
"Timestamp":"$filter{st:value > 75.3}, ${st:time}",
"Value":"${st:value}"
}
}
静态属性(仅当st:Value大于75.3时才对Static_Value属性进行编码)。
{
"Observation":
{
"$source":"st:MeteoObservationsFeature",
"Timestamp":"${st:time}",
"Static_value":"$filter{st:value > 75.3}, this Observation has a value > 75.3",
"Value":"${st:value}"
}
}
从前面的数组和对象情况的示例中可以看出,筛选器语法需要一个 "$filter" 关键字,后跟带有要计算的筛选器的属性。相反,在属性情况下,筛选器在值内指定为 "$filter{...}" ,后跟CQL表达式或静态内容,两者之间用逗号分隔。
GML¶
filter 和 source 在GML模板中也可用。假设所需的输出是上述GeoJSON输出的对应GML等效项,例如:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<wfs:FeatureCollection xmlns:st="http://www.stations.org/1.0" xmlns:xs="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema" xmlns:wfs="http://www.opengis.net/wfs/2.0" xmlns:xlink="http://www.w3.org/1999/xlink" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:gml="http://www.opengis.net/gml/3.2" numberMatched="3" numberReturned="0" timeStamp="2021-07-13T15:09:28.620Z">
<wfs:member>
<st:MeteoStations gml:id="MeteoStationsFeature.7">
<st:code>Station_BOL</st:code>
<st:name>Bologna</st:name>
<st:geometry>
<gml:Point srsName="urn:ogc:def:crs:EPSG::4326" srsDimension="2" gml:id="smdl-stations.1.geom">
<gml:pos>11.34 44.5</gml:pos>
</gml:Point>
</st:geometry>
<st:temperature>
<st:temperature>
<st:Temperature>
<st:time>2016-12-19T11:28:31.000Z</st:time>
<st:value>35.0</st:value>
</st:Temperature>
</st:temperature>
<st:temperature>
<st:Temperature>
<st:time>2016-12-19T11:28:55.000Z</st:time>
<st:value>25.0</st:value>
</st:Temperature>
</st:temperature>
</st:temperature>
<st:pressure>
<st:pressure>
<st:Pressure>
<st:time>2016-12-19T11:30:26.000Z</st:time>
<st:value>1019.0</st:value>
</st:Pressure>
</st:pressure>
<st:pressure>
<st:Pressure>
<st:time>2016-12-19T11:30:51.000Z</st:time>
<st:value>1015.0</st:value>
</st:Pressure>
</st:pressure>
</st:pressure>
<st:wind_speed>
<st:wind_speed>
<st:Wind_speed>
<st:time>2016-12-19T11:29:24.000Z</st:time>
<st:value>80.0</st:value>
</st:Wind_speed>
</st:wind_speed>
</st:wind_speed>
</st:MeteoStations>
</wfs:member>
</wfs:FeatureCollection>
以下GML模板将产生上述输出:
<gft:Template>
<gft:Options>
<gft:Namespaces xmlns:st="http://www.stations.org/1.0"/>
</gft:Options>
<st:MeteoStations gml:id="${@id}">
<st:code>$${strConcat('Station_',st:code)}</st:code>
<st:name>${st:common_name}</st:name>
<st:geometry>${st:position}</st:geometry>
<st:temperature gft:isCollection="true" gft:source="st:meteoObservations/st:MeteoObservationsFeature" gft:filter="xpath('st:meteoParameters/st:MeteoParametersFeature/st:param_name') = 'temperature'">
<st:Temperature>
<st:time>${st:time}</st:time>
<st:value>${st:value}</st:value>
</st:Temperature>
</st:temperature>
<st:pressure gft:isCollection="true" gft:source="st:meteoObservations/st:MeteoObservationsFeature" gft:filter="xpath('st:meteoParameters/st:MeteoParametersFeature/st:param_name') = 'pressure'">
<st:Pressure>
<st:time>${st:time}</st:time>
<st:value>${st:value}</st:value>
</st:Pressure>
</st:pressure>
<st:wind_speed gft:isCollection="true" gft:source="st:meteoObservations/st:MeteoObservationsFeature" gft:filter="xpath('st:meteoParameters/st:MeteoParametersFeature/st:param_name') = 'wind speed'">
<st:Wind_speed>
<st:time>${st:time}</st:time>
<st:value>${st:value}</st:value>
</st:Wind_speed>
</st:wind_speed>
</st:MeteoStations>
</gft:Template>
在GML案例中 filter 和 source 指令的定义方式与JSON用例略有不同。
需要将筛选器定义为属性
gft:filter在要过滤的元素中。需要将源定义为属性
gft:source将为其子元素设置源的元素中。该属性
gft:isCollection="true"定义一个用于在GML模板中标记集合元素的指令:该指令是必需的,因为XML没有数组概念,并且需要通知模板机制是否应该重复某个元素,因为它代表一个集合元素。
对于GeoJSON的情况,顶层特性不需要源代码。在本例中,我们确实为st:MeteoStations元素省略了它。相反,如上所述,它对于嵌套元素是强制的,如 Temperature , Pressure 和 Winds_speed 。所有这些都确实显示出一种 gft:source="st:meteoObservations/st:MeteoObservationsFeature" 。
有关XPath函数的更多信息¶
这个 xpath('xpath') 函数旨在提供引用要素属性的可能性,而无论模板中的嵌套程度如何,还提供了通过引用先前上下文值的可能性 ../ 。
从GeoJSON站点用例中检查以下模板。
{
"$source":"st:MeteoStationsFeature",
"properties":{
"Code":"$${strConcat('STATION-', xpath('st:code'))}",
"Location":"$${toWKT(xpath('st:position'))}",
"Temperatures":[
{
"$source":"st:meteoObservations/st:MeteoObservationsFeature",
"$filter":"xpath('st:meteoParameters/st:MeteoParametersFeature/st:param_name') = 'temperature'"
},
{
"Value": "${st:value}",
"StillCode":"$${strConcat('STATION-', xpath('../st:code'))}"
}
]
}
在 Temperatures 数组a StillCode 属性已定义为 ../ 引用,而不是 "$source":"st:meteoObservations/st:MeteoObservationsFeature" ,但前一次 "$source":"st:MeteoStationsFeature" 。
如果不需要CQL函数求值,则可以使用属性内插指令实现相同的目的: "StillCode":"$${strConcat('STATION-', xpath('../st:code'))}" 。
警告
这个 xpath('some xpath) CQL函数将在此插件的范围内使用。有关一般用法,请参阅 property function 。
模板选项¶
到目前为止看到的指令允许在Feature元素的作用域中控制输出。这个 options 相反,指令允许为功能范围之外的部分输出自定义输出,或定义对整体输出的常规修改。可用选项因输出格式而异。
GeoJSON¶
In the context of a GeoJSON template two options are available: flat_output and separator. These options are meant to provide a GeoJSON output encoded following INSPIRE rule for alternative feature GeoJSON encoding (see also).
To use the functionality an "$options" JSON object can be added on top of a JSON template, like in the following example:
{
"$options":{
"flat_output":true,
"separator": "."
},
"$source":"st:MeteoStationsFeature",
"Identifier":"${@id}",
"geometry":"${st:position}",
"properties":{
"Name":"${st:common_name}",
"Code":"$${strConcat('STATION-', xpath('st:code'))}",
"Location":"$${toWKT(xpath('st:position'))}",
"Temperatures":[
{
"$source":"st:meteoObservations/st:MeteoObservationsFeature",
"$filter":"xpath('st:meteoParameters/st:MeteoParametersFeature/st:param_name') = 'temperature'"
},
{
"Timestamp": "${st:time}",
"Value": "${st:value}"
}
],
"Pressures":[
{
"$source":"st:meteoObservations/st:MeteoObservationsFeature",
"$filter":"xpath('st:meteoParameters/st:MeteoParametersFeature/st:param_name') = 'pressure'"
},
{
"Timestamp": "${st:time}",
"Value": "${st:value}"
}
],
"Winds_speed":[
{
"$source":"st:meteoObservations/st:MeteoObservationsFeature",
"$filter":"xpath('st:meteoParameters/st:MeteoParametersFeature/st:param_name') = 'wind speed'"
},
{
"Timestamp": "${st:time}",
"Value": "${st:value}"
}
]
}
}
这个 flat_output 将采取以下行动:
将跳过对嵌套数组和对象的编码,只对其属性进行编码。
对象属性名称将与其json属性的名称连接在一起。
数组的属性名称也将与其内部对象的一个json属性连接在一起。此外,每个嵌套对象的数组属性名称后都会添加一个索引值。
这个
separator指定属性名称的分隔符。缺省值为_。最终输出将有一个属性的平面列表,这些属性的名称由串联生成,如下所示。
JSON-LD¶
JSON-LD模板可以定义为GeoJSON模板,因为它也是基于JSON的输出。但是,它需要有一个 @context 属性、对象或数组位于其开头,以符合标准。此外,每个JSON对象都必须有一个 @type 通过词汇表术语定义类型。要实现这些要求,可以指定几个 $options 在模板上:
@context提供完整的JSON-LD@context。@type在最终输出中为根JSON对象提供类型术语(缺省情况下,该值为FeatureCollection)。collection_name在最终输出中为要素数组提供替代名称(默认情况下features是使用的)。如果用户希望使用与词汇表中定义的特定术语相同的功能属性名称,则该选项非常有用。
{
"$options":{
"encode_as_string": true,
"collection_name":"stations",
"@type":"schema:Thing",
"@context":[
"https://opengeospatial.github.io/ELFIE/contexts/elfie-2/elf-index.jsonld",
"https://opengeospatial.github.io/ELFIE/contexts/elfie-2/gwml2.jsonld",
{
"gsp":"http://www.opengis.net/ont/geosparql#",
"sf":"http://www.opengis.net/ont/sf#",
"schema":"https://schema.org/",
"st":"http://www.stations.org/1.0",
"wkt":"gsp:asWKT",
"Feature":"gsp:Feature",
"geometry":"gsp:hasGeometry",
"point":"sf:point",
"features":{
"@container":"@set",
"@id":"schema:hasPart"
}
}
]
},
"$source":"st:MeteoStationsFeature",
"Identifier":"${@id}",
"Name":"${st:common_name}",
"Code":"$${strConcat('STATION-', xpath('st:code'))}",
"Location":"$${toWKT(st:position)}",
"Temperatures":[
{
"$source":"st:meteoObservations/st:MeteoObservationsFeature",
"$filter":"xpath('st:meteoParameters/st:MeteoParametersFeature/st:param_name') = 'temperature' AND 'yes' = env('showTemperatures','yes')"
},
{
"Timestamp":"${st:time}",
"Value":"${st:value}"
}
],
"Pressures":[
{
"$source":"st:meteoObservations/st:MeteoObservationsFeature",
"$filter":"xpath('st:meteoParameters/st:MeteoParametersFeature/st:param_name') = 'pressure' AND 'yes' = env('showPressures','yes')"
},
{
"Timestamp":"${st:time}",
"Value":"${st:value}"
}
],
"Winds speed":[
{
"$source":"st:meteoObservations/st:MeteoObservationsFeature",
"$filter":"xpath('st:meteoParameters/st:MeteoParametersFeature/st:param_name') = 'wind speed' AND 'yes' = env('showWinds','yes')"
},
{
"Timestamp":"${st:time}",
"Value":"${st:value}"
}
]
}
这个 @context 将显示在JSON-LD输出的开头:
{
"@context":[
"https://opengeospatial.github.io/ELFIE/contexts/elfie-2/elf-index.jsonld",
"https://opengeospatial.github.io/ELFIE/contexts/elfie-2/gwml2.jsonld",
{
"gsp":"http://www.opengis.net/ont/geosparql#",
"sf":"http://www.opengis.net/ont/sf#",
"schema":"https://schema.org/",
"st":"http://www.stations.org/1.0",
"wkt":"gsp:asWKT",
"Feature":"gsp:Feature",
"geometry":"gsp:hasGeometry",
"point":"sf:point",
"features":{
"@container":"@set",
"@id":"schema:hasPart"
}
}
],
"type":"FeatureCollection",
"@type":"schema:Thing",
"stations":[
{
"Identifier":"MeteoStationsFeature.7",
"Name":"Bologna",
"Code":"STATION-BOL",
"Location":"POINT (44.5 11.34)",
"Temperatures":[
{
"Timestamp":"2016-12-19T11:28:31.000+00:00",
"Value":"35.0"
},
{
"Timestamp":"2016-12-19T11:28:55.000+00:00",
"Value":"25.0"
}
],
"Pressures":[
{
"Timestamp":"2016-12-19T11:30:26.000+00:00",
"Value":"1019.0"
},
{
"Timestamp":"2016-12-19T11:30:51.000+00:00",
"Value":"1015.0"
}
],
"Winds speed":[
{
"Timestamp":"2016-12-19T11:29:24.000+00:00",
"Value":"80.0"
}
]
}
]
}
上面的模板定义了 @context ,也是 option encode_as_string 。该选项用于请求JSON-LD输出,其中所有属性都编码为文本。默认情况下,属性的编码方式为 GeoJSON 输出格式。
在处理通过LayerGroup请求JSON-LD输出的GetFeatureInfo请求时,插件将执行JSON-LD的联合 @context (如果不同)在每个包含的层的模板中定义。这意味着在属性名称冲突的情况下,属性名称将根据层的处理顺序相互覆盖。用户可以通过利用 include 指令,如下所述,定义单个 @context 包括在每个包含层的模板中。这样,所有层都将共享相同的上下文定义。
GML¶
GML输出有两个 options :命名空间和架构位置,它们定义了将包含在结果输出的FeatureCollection元素中的命名空间和架构位置属性。这些选项需要在 gft:Options 元素位于模板开头,紧跟在 gft:Template 元素,例如
<gft:Template>
<gft:Options>
<gft:Namespaces xmlns:st="http://www.stations.org/1.0"/>
<gft:SchemaLocation xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.stations.org/1.0 http://www.stations.org/stations/1.0/xsd/stations.xsd"/>
</gft:Options>
<st:MeteoStations gml:id="${@id}">
<st:code>$${strConcat('Station_',st:code)}</st:code>
<st:name>${st:common_name}</st:name>
<st:geometry>${st:position}</st:geometry>
<st:temperature gft:isCollection="true" gft:source="st:meteoObservations/st:MeteoObservationsFeature" gft:filter="xpath('st:meteoParameters/st:MeteoParametersFeature/st:param_name') = 'temperature'">
<st:Temperature>
<st:time>${st:time}</st:time>
<st:value>${st:value}</st:value>
</st:Temperature>
</st:temperature>
<st:pressure gft:isCollection="true" gft:source="st:meteoObservations/st:MeteoObservationsFeature" gft:filter="xpath('st:meteoParameters/st:MeteoParametersFeature/st:param_name') = 'pressure'">
<st:Pressure>
<st:time>${st:time}</st:time>
<st:value>${st:value}</st:value>
</st:Pressure>
</st:pressure>
<st:wind_speed gft:isCollection="true" gft:source="st:meteoObservations/st:MeteoObservationsFeature" gft:filter="xpath('st:meteoParameters/st:MeteoParametersFeature/st:param_name') = 'wind speed'">
<st:Wind_speed>
<st:time>${st:time}</st:time>
<st:value>${st:value}</st:value>
</st:Wind_speed>
</st:wind_speed>
</st:MeteoStations>
</gft:Template>
HTML¶
Html模板可以使用多个 options :
<script>允许定义所需的任何Java脚本,例如创建树视图(如下例所示)或Open Layers地图客户端。- 编码:
<script type="application/ld+json"/> 中模板的特性的JSON-LD表示形式 <head> 。为了使选项正常工作,必须为该层配置JSON-LD模板,否则Geoserver将返回错误消息。
<style>允许定义css内容。<link>允许链接到外部资源。
的内容 <script> 和 <style> 需要以下列形式提供 <![CDATA[ 。
以下是将桩号要素输出为树视图的HTML模板样例。同样在本例中,我们在 st:meteoObservations 与其他模板示例相同。::
<gft:Template>
<gft:Options>
<style>
<![CDATA[ul, #myUL {
list-style-type: none;
}
#myUL {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
}
.caret {
cursor: pointer;
-webkit-user-select: none; /* Safari 3.1+ */
-moz-user-select: none; /* Firefox 2+ */
-ms-user-select: none; /* IE 10+ */
user-select: none;
}
.caret::before {
content: "\25B6";
color: black;
display: inline-block;
margin-right: 6px;
}
.caret-down::before {
-ms-transform: rotate(90deg); /* IE 9 */
-webkit-transform: rotate(90deg); /* Safari */'
transform: rotate(90deg);
}
.nested {
display: none;
}
.active {
display: block;
}]]></style>
<script><![CDATA[window.onload = function() {
var toggler = document.getElementsByClassName("caret");
for (let item of toggler){
item.addEventListener("click", function() {
this.parentElement.querySelector(".nested").classList.toggle("active");
this.classList.toggle("caret-down");
});
}
}]]></script>
<script type="application/ld+json"/>
</gft:Options>
<ul id="myUL">
<li>
<span class="caret">MeteoStations</span>
<ul class="nested">
<li>
<span class="caret">Code</span>
<ul class="nested">
<li>$${strConcat('Station_',st:code)}</li>
</ul>
</li>
<li>
<span class="caret">Name</span>
<ul class="nested">
<li>${st:common_name}</li>
</ul>
</li>
<li>
<span class="caret">Geometry</span>
<ul class="nested">
<li>${st:position}</li>
</ul>
</li>
<li gft:isCollection="true" gft:source="st:meteoObservations/st:MeteoObservationsFeature" gft:filter="xpath('st:meteoParameters/st:MeteoParametersFeature/st:param_name') = 'temperature'">
<span class="caret">Temperature</span>
<ul class="nested">
<li>
<span class="caret">Time</span>
<ul class="nested">
<li>${st:time}</li>
</ul>
</li>
<li>
<span class="caret">Value</span>
<ul class="nested">
<li>${st:time}</li>
</ul>
</li>
</ul>
</li>
<li gft:isCollection="true" gft:source="st:meteoObservations/st:MeteoObservationsFeature" gft:filter="xpath('st:meteoParameters/st:MeteoParametersFeature/st:param_name') = 'pressure'">
<span class="caret">Pressure</span>
<ul class="nested">
<li>
<span class="caret">Time</span>
<ul class="nested">
<li>${st:time}</li>
</ul>
</li>
<li>
<span class="caret">Value</span>
<ul class="nested">
<li>${st:time}</li>
</ul>
</li>
</ul>
</li>
<li gft:isCollection="true" gft:source="st:meteoObservations/st:MeteoObservationsFeature" gft:filter="xpath('st:meteoParameters/st:MeteoParametersFeature/st:param_name') = 'wind speed'">
<span class="caret">Wind Speed</span>
<ul class="nested">
<li>
<span class="caret">Time</span>
<ul class="nested">
<li>${st:time}</li>
</ul>
</li>
<li>
<span class="caret">Value</span>
<ul class="nested">
<li>${st:time}</li>
</ul>
</li>
</ul>
</li>
</ul>
</li>
</ul>
</gft:Template>
模板的输出如下所示:

包括其他模板¶
在开发一组模板时,可能会注意到跨不同模板实例重复的部分。模板包含允许共享公共部分,将它们提取到可重复使用的构建块中。
可以使用两个指令执行包含:
include允许按原样包括单独的模板。includeFlat允许包括单独的模板,剥离最顶部的容器。
至于其他指令,基于JSON的模板和基于XML的指令的语法略有不同。
这两个指令需要指定要包含的模板的路径。模板名称可以是普通的,如本例所示,指代子目录,也可以是绝对的。有效模板引用的示例包括:
subProperty.json./subProperty.json./blocks/aBlock.json/templates/test/aBlock.json
但是,目前还不能使用相对引用在目录层次结构中向上攀登,因此 ../myParentBlock.json 将被拒绝。
基于JSON的模板(GeoJSON、JSON-LD)¶
在这种情况下,这两个指令可以定义为:
$include。$includeFlat。
关于 $includeFlat 选项值得一提的是,在JSON上下文中:
如果包含JSON对象,则直接就地包含其属性,只有在另一个对象中才有意义。
如果包含JSON数组,则直接就地包含其值,只有在另一个数组中才有意义。
以下JSON代码片段显示了模板包含的四个可能的语法选项:
1 {
2 "aProperty": "$include{subProperty.json}",
3 "$includeFlat": "propsInAnObject.json",
4 "anArray" : [
5 "$include{arrayElement.json}",
6 "$includeFlat{subArray.json}"
7 ],
8 "$includeFlat": "${property}"
9 }
备注:
这个
subProperty.json模板(第2行)既可以是对象,也可以是数组,它将用作aProperty这个
propsInAnObject.json模板(第3行)需要是JSON对象,其属性将直接包含在$includeFlat指令IS这个
arrayElement.json模板(第5行)既可以是对象,也可以是数组,值将直接替换为中的新元素anArray。这允许创建JSON对象作为数组元素,或创建嵌套数组。这个
subArray.json模板(第6行)本身必须是一个数组,容器数组将被剥离,其值直接集成在其中anArray。
如果指定了include deFlat指令,并且其属性值是属性内插指令,则如果属性名称的计算结果为json,则它将包含在最终输出中,例如
包括json:
1 {
2 "property":"${property}",
3 "bProperty":"15",
4 "cProperty":"30"
5 }
${Property}值:
1 {
2 "aProperty": "10",
3 "bProperty": "20"
4 }
结果:
1 {
2 "aProperty":"10",
3 "bProperty":"20",
4 "cProperty":"30"
5 }
这个 ${property} 指令的计算结果为JSON,该JSON将与包含的JSON合并。如果将JSON作为名称与包含的JSON中的某个属性相同的属性包含,则包含的JSON将覆盖包含的JSON中同名的属性。
如果在具有Feature属性的JSON数组内指定了cluddeFlat指令,并且该属性的计算结果为JSON数组,则容器数组将被剥离,其值将直接包含在容器数组中:
1 [
2 "value1",
3 "value2",
4 "value3",
5 "$includeFlat{${property}}"
6 ]
${Property}值:
1 [
2 "value4",
3 "value5"
4 ]
结果:
1 [
2 "value1",
3 "value2",
4 "value3",
5 "value4",
6 "value5"
7 ]
基于XML的模板(GML)¶
在XML上下文中,这两个指令需要按以下方式定义:
<gft:includeFlat>path/to/included.xml</gft:includeFlat>。<gsml:specification gft:source="gsml:specification">$include{includedTemplate.xml}</gsml:specification>。
在第一种情况下,包含的模板将替换 <gft:includeFlat> 元素。在第二个示例中,包含的模板将放置在 <gsml:specification> 元素。
通过合并扩展其他模板(仅限基于JSON的模板)¶
如上所述,模板包含允许按原样将块导入到另一个模板。这个 $merge 指令允许获取一个对象并将其用作基对象,该对象将被其合并到的对象的属性覆盖。
例如,让我们假设这是一个基本JSON模板:
{
"a": 10,
"b": "${attribute1}",
"c": "${attribute2}",
"array": [1, 2, 3]
}
这是一个扩展它的模板:
{
"$merge": "base.json",
"a": {
"a1": 1,
"a2": 2
},
"b": null,
"d": "${customAttribute}"
}
实际正在处理的模板如下所示:
{
"a": {
"a1": 1,
"a2": 2
},
"c": "${attribute2}",
"array": [1, 2, 3]
"d": "${customAttribute}"
}
对象合并的一般规则如下:
被重写的简单属性将被替换。
将删除设置为NULL的属性。
向下钻取两个树中可用的嵌套对象,并递归合并。
数组按原样替换,不合并。最终的顶层
features数组是此规则的唯一例外。虽然键的顺序在JSON中并不重要,但合并是这样处理的,即在合并结果中首先包含基本属性名称,然后在它们之后添加覆盖中包含的新属性名称。
如果在Overalay JSON模板中,存在带有属性内插指令的属性或返回JSON的表达式,则JSON属性树也将与基本JSON树中的相应属性合并。
这个 $merge 指令可以在任何对象中使用,使其成为合并操作的根。当需要本地自定义时,这可以用作包含的替代方案。
环境参数化¶
还可以动态地操作模板配置,使用 env 参数。要实现这一点,属性名、属性或源应该用env函数替换,方法如下 $${{env('nameOfTheEnvParameter','defaultValue')}} . 如果在请求中指定了env query参数 env='nameOfTheEnvParameter':'newValue' ,则最终输出中的默认值将替换为请求中指定的值。
该功能还允许动态操作过滤器和表达式。例如,可以更改过滤器参数: "$filter":"xpath('gsml:name') = env('nameOfTheEnvParameter','defaultValue') .
xpath也可以被完全或部分替换: $${{xpath(env('xpath','gsml:ControlledConcept/gsml:name')}} 或 $${{xpath(strConcat('env('gsml:ControlledConcept',xpath','/gsml:name')))}} .
动态关键点¶
JSON输出中的键也可以完全依赖于功能属性,例如:
{
"${attributeA}" : "${attributeB}",
"$${strSubstring(attributeC, 0, 3)}": "$${att1 * att2}"
}
然而,根据功能属性使用键有缺点:它不可能用于WFS中的过滤和OGCAPI中的可查询生成,因为它没有稳定的值。
基于JSON的属性¶
某些数据库具有对JSON字段的本机支持。例如,PostgreSQL既有JSON类型,也有JSONB类型。JSON模板机制可以识别这些字段并将它们导出为JSON块,以便在输出中直接替换。
还可以选择一个JSON属性并使用 jsonPointer 函数从中提取属性或整个JSON子树。请参阅 JSON Pointer RFC 有关有效表达式的更多详细信息,请参见。
以下是使用JSON属性的示例:
1{
2 "assets": "${assets}",
3 "links": [
4 "$${jsonPointer(others, '/fullLink')}",
5 {
6 "href": "$${jsonPointer(others, '/otherLink/href')}",
7 "rel": "metadata",
8 "title": "$${jsonPointer(others, '/otherLink/title')}",
9 "type": "text/xml"
10 }
11 ]
12}
一些参考资料:
Line 1用途assets,该属性可以包含任何形状的JSON树,该树将被原地展开。Line 4在数组中插入完整的JSON对象。该对象是others属性,这是一个具有多个额外属性的复杂JSON文档(可能是不适合固定数据库模式的属性的通用容器)。Line 6和Line 8摘录自others属性特定的字符串值。
基于数组的属性(仅限基于JSON的模板)¶
在JSON属性中,现代数据库中支持基于数组的属性的情况并不少见。例如。 varchar[] 是包含字符串数组的属性。
数组属性可以按原样使用,它们将扩展为JSON数组。让我们假设 keywords 数据库列包含一个字符串列表,然后是以下模板:
1{
2 "keywords": "${keywords}"
3}
可能扩展为:
1{
2 "keywords": ["features", "templating"]
3}
也可以使用数组作为迭代源,使用 ${.} XPath。例如:
1{
2 "metadata": [
3 {
4 "$source": "keywords"
5 },
6 {
7 "type": "keyword",
8 "value": "${.}"
9 }
10 ]
11}
以上内容可能扩展为:
1{
2 "metadata": [
3 {
4 "type": "keyword",
5 "value": "features"
6 },
7 {
8 "type": "keyword",
9 "value": "templating"
10 }
11 ]
12}
如果需要检索数组的特定项,则 item 函数可以使用,例如,以下模板提取数组中的第二项(如果不存在将失败):
1{
2 "second": "$${item(keywords, 1)}"
3}
目前,GML模板中没有显式支持基于数组的列。
简化的属性访问¶
要素模板化插件提供了在处理复杂要素和使用模板中的属性内插时直接引用域名的可能性。作为一个例子,让我们再次使用流星站用例。这是所涉及的数据库表的ER图。

下面是一个GeoJSON模板,它直接引用表名和列名,而不是在AppSchema映射中引用目标XPath。
{
"$source":"meteo_stations",
"Identifier":"${id}",
"Name":"${common_name}",
"Code":"$${strConcat('STATION-', xpath('code'))}",
"Location":"$${toWKT(position)}",
"Temperatures":[
{
"$source":"meteo_observations",
"$filter":"propertyPath('->meteo_parameters.param_name') = 'temperature' AND 'yes' = env('showTemperatures','yes')"
},
{
"Timestamp":"${time}",
"Value":"${value}"
}
],
"Pressures":[
{
"$source":"meteo_observations",
"$filter":"propertyPath('->meteo_parameters.param_name') = 'pressure' AND 'yes' = env('showPressures','yes')"
},
{
"Timestamp":"${time}",
"Value":"${value}"
}
],
"Winds speed":[
{
"$source":"meteo_observations",
"$filter":"propertyPath('->meteo_parameters.param_name') = 'wind speed' AND 'yes' = env('showWinds','yes')"
},
{
"Timestamp":"${time}",
"Value":"${value}"
}
]
}
可以看出,与上面看到的模板相比,此模板有一些不同:
属性内插 (
${property})和CQL评估 ($${cql})指令引用要包含在最终输出中的属性的列名。名称与列中的名称匹配,并且没有使用名称空间前缀。Inside the $${cql} directive instead of using an
xpathfunction thepropertyPathfunction is being use. It must be used when the property references domain names inside a$${cql}directive. Paths in this case are no more separated by a/but by a.dot.这个
$source指令引用表名。当一个
column/propertyin atable/sourceis referenced from the context of the uppertable/source, as in all the filters in the template, the table name needs to be prefixed with a->symbol, and column name can come next separated by a.多特。换一种说法:->表示下一个路径部分是连接到最后定义的源的表。
警告
这个 propertyPath('propertyPath') CQL函数仅在此插件的范围内使用。目前不能在模板文件的上下文之外引用域属性。
在基于Smart Data Loader的复杂功能之上定义模板时,此功能特别有用。
控制具有N个基数的属性¶
当属性内插针对复杂要素中具有多个基数的属性时,要素模板将以数组形式输出结果。可以通过使用插件中提供的一组CQL函数来控制和修改此默认行为,这些函数允许控制列表在模板中的编码方式。
aggregate:将返回值列表的表达式(属性名称或函数)和聚合类型的文字作为参数,例如。aggregate(my.property.name,'MIN')。支持的聚合类型如下:MIN将返回数值列表中的最小值。MAX将返回数值列表中的最大值。AVG将返回数值列表中的平均值。UNIQUE将从值列表中删除重复值。JOIN将在单个字符串中串联值列表。它接受一个参数来指定分隔符,该分隔符默认情况下为空格:aggregate(my.property.name,'JOIN(,)')。
stream:接受未定义数量的表达式作为参数,并链接它们,以便每个表达式在前一个表达式的输出上求值:例如。stream(aPropertyName,aFunction,anotherPropertyName)同时评估aFunction关于…的输出aPropertyName评估,并最终anotherPropertyName将根据以下结果进行评估aFunction。filter:将文字cql筛选器作为参数并对其求值。Cql筛选器中的每个字符串文字值必须位于转义的双引号之间:例如。filter('aProperty = \"someValue\"')。sort:按升序或降序对值列表进行排序。它接受排序顺序作为参数 (ASC,DESC)以及可选的属性名称,以确定应该对其执行排序的属性。如果未定义属性名称,则排序将应用于函数计算的当前节点:sort('DESC',nested.property),sort('ASC')。
上面的函数可以组合在一起,允许对模板中列表值的编码进行细粒度控制。假设要为 meteo stations use case 下面是函数用法的一些示例(下面的示例中使用简化的属性访问):
aggregate(stream(->meteo_observations,filter('value > 35')),AVG)将计算并返回所有观测嵌套要素值属性的平均值。aggregate(stream(->meteo_observations.->meteo_parameters,sort("ASC",param_name),param_unit),JOIN(,))将会拿起meteo_parameter每个站点要素的嵌套要素将根据param_name并将串接param_unit单个字符串中的值,用逗号分隔。
模板验证¶
有两种验证可用。每次第一次请求模板或在发生修改后,第一个操作都会自动完成。它由Geoserver自动完成,并验证模板中使用的所有特性名称是否适用于要素类型。第二种类型的验证可以在请求JSON-LD或GML输出的情况下从UI发出(参见配置部分)。GML验证将对照提供的 SchemaLocation 价值观。这个 JSON-LD 验证详细如下。
JSON-LD验证¶
该插件提供了对json-id输出的验证 @context 在模板中定义。可以通过在请求中指定新的查询参数来请求它: validation=true 。该验证利用json-ld API并执行以下步骤:
这个 expansion algorithm 对json ld输出执行,将每个特性的属性名扩展为IRIs,删除在
@context以及@context本身;这个 compaction algorithm 然后对展开结果执行,将
@context并将扩展的属性名缩短为原始输出中的术语;最后,将压缩过程的结果与原始json ld进行比较,如果缺少某些属性,则表示在
@context. 异常被抛出,消息指向缺少的属性。